Member
-
Atsushi Momose
Professor / Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM), Tohoku University.
- Career Summary
Mar.1985 Graduated, Faculty of Engineering, The University of Tokyo Mar.1987 Master of Engineering from The University of Tokyo Apr.1987-Oct.1999 Advanced Research Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Mar.1997-Feb.1998 Visitor Scientist, European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (Grenoble, France) Nov.1999-Mar. 2012 Associate Professor, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo Mar.2003-Mar. 2012 Associate Professor, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo Apr. 2012- Professor, Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials (IMRAM), Tohoku University
- Educational Activities
Graduate School: Introduction to Advanced Materials Science I, Quantum Beam
Undergraduate: Electrodynamics II, Fundamentals in Physics Experiments I
- Reserch Activities
X-rays, which are electromagnetic waves of extremely short wavelengths, are widely used both in fundamental research and in applications as indispensable probes for measurements. Synchrotron radiation (SR) sources, which are currently the most advanced X-ray sources, have accelerated the developments of X-ray technology. The brilliance of SR is roughly 10 billion times higher than that of laboratory X-ray generators. In addition, SR has attractive properties that are very difficult to realize in laboratories; these include wavelength selectivity, coherence, polarization, and pulse structure. Our ambition is to pioneer the frontiers of SR-based techniques, particularly by using X-ray phase information.
Our current interest is to innovate X-ray imaging by developing X-ray phase-contrast techniques. X-ray radiography is a familiar technique; for instance, it is used in hospitals as one modality for clinical diagnosis. The sensitivity of X-ray radiography to soft tissues, however, is inherently poor. By contrast, a 1000-times higher sensitivity can be attained by utilizing X-ray phase information (ref.1), allowing us to image soft tissues, such as cancerous tumors.
We have developed X-ray phase imaging methods based on phase measurement using X-ray interferometers (refs. 2 & 3). Three-dimensional observation can also be performed by using X-ray phase imaging in combination with X-ray computed tomography (see Figure). We have demonstrated that tumors and blood vessels can be imaged without using contrast media (refs. 2 & 3).
In addition to fundamental work in X-ray optics, we are also interested in developing phase imaging systems for actual applications. For this, we need to develop a new phase-imaging method that does not require a SR source, which is a huge facility that is only located at limited sites. We have shown that X-ray Talbot(-Lau) interferometry, which employs transmission X-ray gratings, can be feasibly combined with a laboratory X-ray generator (ref. 4). Our work in X-ray phase imaging is currently supported by the project "Development of medical phase imaging system using high-aspect-ratio X-ray gratings" (2007-) of SENTAN, JST.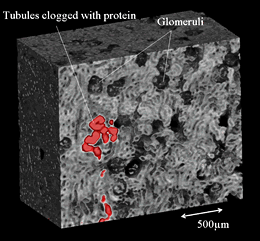
Phase tomogram obtained from the tissue of a rat kidney
[Literature]
1) A. Momose and J. Fukuda, Med. Phys. 22 (1995) 375.
2) A. Momose et al., Nature Medicine 2 (1996) 473.
3) A. Momose et al., Radiology 217 (2000) 593.
4) A. Momose et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 42 (2003) L866. - Other Activities
The Japanese Society for Synchrotron Radiation Research (Secretary of General Affairs)
The Physical Society of Japan
The Japan Society of Applied Physics
The Society of Polymer Science, Japan
Japan Society of Medical Physics
The International Society of Optical Engineering (SPIE)
- Future Plan
Our research and education are oriented not only to fundamental X-ray science but also to technical developments for various applications, particularly using modern X-ray sources, such as SR, and, in the near future, X-ray free-electron lasers. Based on our technology "eye for seeing X-ray phase", we aim to establish a center of excellence in X-ray optics.
- Messages to students
Imagine yourself in the coming decades. Hopefully, you may be active on the internatinal stage of science. As you face the future, be vigorous, keen to discuss things, sensitive to originality, and active.