Neutron phase imaging
Neutron radiography is one of the methods for visualizing the inside of matter. Because neutrons have a higher penetrating power to matter than X-rays and interact with matter differently from X-rays, neutron radiography is used for unique purposes.
Neutrons have wave nature with de Broglie wavelengths. The wavelengths are comparable to those of X-rays, and the concept of X-ray phase imaging can be extended to neutron radiography. To implement this idea, we started research by developing neutron gratings. For X-ray gratings, Au is used because the technology of electroplating is established. However, Au is not effective for neutrons. Because Gd has an exceptionally high absorption coefficient for neutrons, we developed Gd gratings. Note that a high aspect-ratio structure should be fabricated since the grating period should be several microns. Furthermore, the grating area that determines the field of view of imaging should be as large as possible.
Figure 1 shows a high aspect-ratio Gd grating developed by refined approach of inclined Gd evaporation [1]. First, a Si grating was fabricated by D-RIE, and then the process of Gd evaporation was designed so that Gd is deposited rectangularly on the shoulder of Si lamellae.
This grating is used for neutron phase imaging at RADEN, J-PARC and a compact neutron source (RANS, Riken).
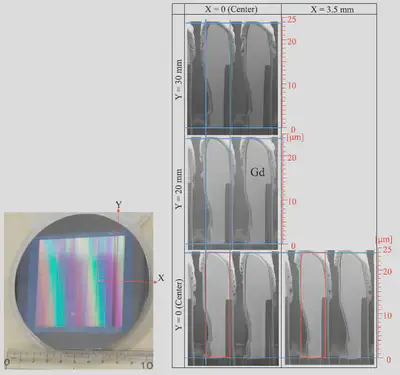
-
[1] T. Samoto et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 58 (2019) SDDF12. DOI: 10.7567/1347-4065/ab138d ↩︎